What is a digital telephone line?

A digital telephone line or digital trunk is a type of telephone line that carries voice and/or data by using digital sampling. By converting analog signals to digital, these types of trunks allow for more information to be transferred over a single connection. For instance the maximum speed of an analog modem is 56 Kilobits per second (Kbps) while the maximum speed of a digital T1 line is 1.544 Megabits per second (Mbps) – almost 30 times more.
How does a digital telephone line work?
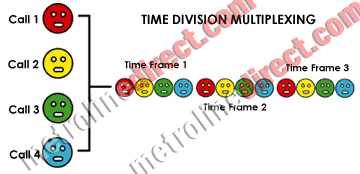
Digital telephone lines use Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), a method of transmitting multiple digital signals over one communication media, to accommodate up to 24 voice conversations over one circuit. The most common digital telephone lines are T1 and Primary Rate Interface (PRI). They are the typical method in which larger offices with considerable call volumes receive telecommunication services.
T1 vs. PRI
PRI is also known as ISDN PRI. ISDN stands for Integrated Services Digital Network. There are two speeds of service offered: BRI or Basic Rate Interface and PRI or Primary Rate Interface. BRI is a low capacity service intended for residential and small business applications. PRI is the high capacity service carried on T1 trunk lines between telco central offices and your location.
PRI divides a T1 digital signal into 24 channels of 64 Kbps capacity per channel. 23 of these channels can be assigned as one telephone call each, the equivalent of having 23 separate telephone lines. The 24th channel is used for signaling information and special features such as caller ID. It is a popular service for call centers which need the ANI automatic number identification or caller ID data.
T1 service can be provided as channelized or unchannelized. In the channelized T1 version, there are 24 channels. Each channel can be a telephone call. T1 gives you 24 phone lines in place of the 23 that can be accommodated with PRI. However, since there is no separate signaling channel, the signaling information that tells when a phone is on hook or off hook is carried within each channel by using or "robbing" the least significant bit. Unfortunately, channelized T1 doesn't provide any capability for ANI or caller ID data. You need PRI service for that.
Networking your companies phone systems
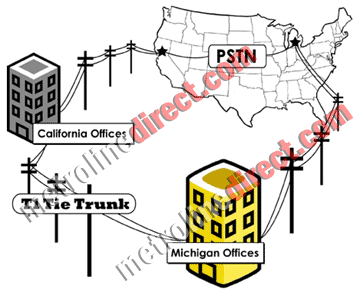
T1 circuits can also be used to network remote phone systems within the same company. For instance an office in Michigan can be networked using a T1 tie trunk to another office in California. A user in Michigan can then connect to a user in California simply by dialing their extension number. This bypasses tolls and allows employees in the business to communicate seamlessly. Routing tables can also be set up to find the most cost effective ways to distribute calls through the Michigan and California offices.
Can my phone system handle a T1?
PBXs that service the SMB and enterprise class markets can accommodate both analog and digital telephone lines. This allows business to grow from a few incoming lines and handful of extensions to multiple T1/PRI lines and a hundreds of extensions. Most SMB PBXs allow up to 3 T1/PRI circuits while enterprise class systems can add many more. To make sure that your PBX is compatible with T1/PRI reference your system manuals, consult with your installation professional, or contact the manufacturer.
When should I consider ordering T1/PRI?
Analog telephone lines should be considered for small and medium sized businesses that require up to 15 incoming lines. When more than 15 are required, a T1/PRI is usually a better choice in terms of both cost and features.